In the newest edition of
DAQ dictionary, we explain terms starting with M and N. We're at the half of the alphabet already and I bet
data acquisition seems closer now.
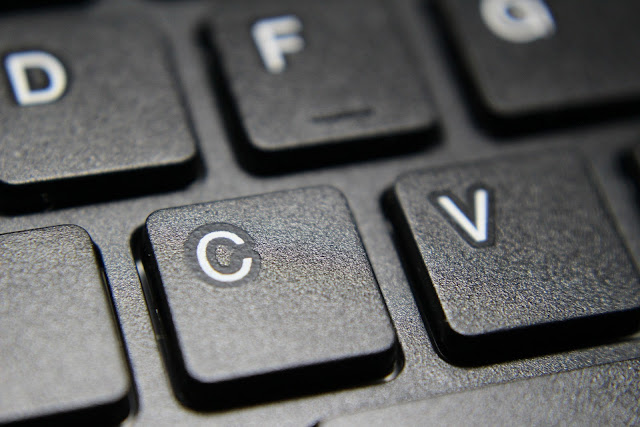
m
The symbol for meter also used to indicate a thousandth part of something (milli)
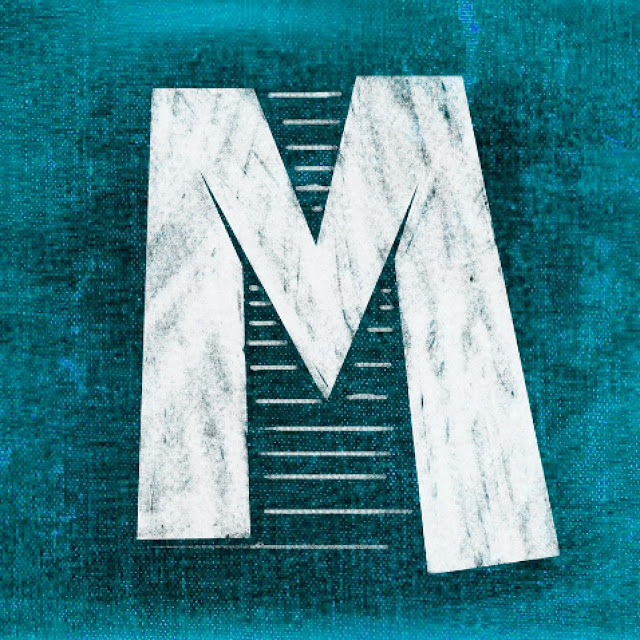
M
The symbol for mega (million).
Mains
The source of electrical power, normally the electricity supply system.
Mains Frequency
Electricity AC supply frequency; 50 Hz in the UK, 60 Hz in the US.
MES
Manufacturing Execution System.
Metre
The SI fundamental unit of length, equal to 1.093 yards. (Meter in US.)
MIS
Manufacturing Information System.
MMI
Man Machine Interface. Also known as the human-machine interface. The
communication between the computer system and the people who use it.
Modular
A form of construction in which hardware or software units, often with differing functions, are quickly interchangeable.
Multiplexing
Where each signal is switched in turn to a single analogue-to-digital
converter. As opposed to where one A-D converter is used for each
signal in simultaneous sampling.
Modbus
An industrial networking system that uses peer-to-peer communications. More details on Modbus are in Issue 32 of Monitor.
Most Significant Bit, MSB
In a binary number, the 1 or 0 furthest to the left.
N-Type Thermocouple
Nicrosil-Nisil thermocouple with a temperature range of -200 to 1200 oC.
Name Server
When communicating with instruments over a TCP-IP network, and your
computer wishes to send a message to a named destination, it asks a Name
Server to resolve the name to an IP Address. Your computer needs to
know the IP Address of the Name Server. You can view this in the TCP/IP
properties of the computer.
Negative Edge Trigger
Data acquisition starts when an input signal changes from a high to a low state.
Network
The physical interconnection of devices sharing a communications protocol.
Node
A device with a direct point of access to a network.
Noise
Any unwanted electrical signals contaminating the signal to be
measured. This noise may be electronic noise which is an artifact of
semiconductor construction techniques and is not
reducible.Alternatively, the noise may be caused by environmental
factors. This type of noise can be the result of poor positioning or
screening of signal wiring. This may result in mains frequency or RF
pickup contaminating the required signal.
Non-Conforming
A product outside manufacturing limits but not necessarily defective.
Non-Destructive Testing
The method of inspecting materials and products without affecting their subsequent properties and performance. Abbreviation NDT.